Algebra Essentials
Algebra is the generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic operations. This ability to manipulate algebraic structures is relavant to many branches of mathematics and empirical sciences.
Types of Numbers
| Name | Symbol | Set | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Numbers | Counting numbers | ||
| Whole Numbers | or | Includes zero | |
| Integers | Includes negative numbers | ||
| Rational Numbers | and and | Can be represented as a fraction | |
| Irrational Numbers | Cannot be represented as a fraction | ||
| Real Numbers | Both rational and irrational numbers combined |
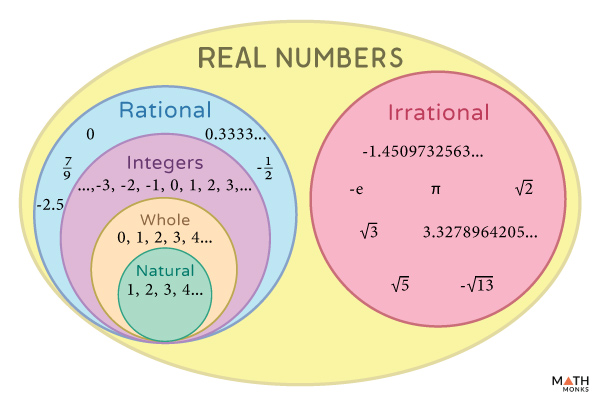
note
There are various sets that are a subset of another. These include:
Types of Decimals
Fractions when converted into decimals come in two forms...
- A terminating decimal has a defined terminating point ().
- A repeating decimal has no terminating point (). A bar is used to denote that those numbers repeat forever.
Order of Operations
The order is as follows...
- Paranthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication or Division
- Addition or Subtraction
Properties of Real Numbers
| Property | Definition |
|---|---|
| Commutative Property of Addition | |
| Commutative Property of Multiplication | |
| Associative Property of Addition | |
| Associative Property of Multiplication | |
| Distributive Property | |
| Identity Property of Addition | |
| Identity Property of Multiplication | |
| Inverse Property of Addition | |
| Inverse Property of Multiplication |
Algebraic Terms
These are commonly encountered terms in algebra...
- A constant is a value that does not vary ().
- A variable represented a value that can vary and is often represented using an alphabetical letter ().
- An algebraic expression is a collection of constants and variables joined together by algebraic operations ().
- An equation is a mathematical statement which indicates that two expressions are equal ().
- A formula is an equation expressing a relationship between constants and variable quantities ( which is the area of a circle).